Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is one of the most common cause of preventable deaths in hospitalized patients. It is associated w/ a mortality rate of 4-13% (when treated) and up to 30% when not treated
More than just its fatality, PE’s are debilitating diseases
- pulmonary hypertension
- post-phlebetic syndrome
In surgical patients need to balance out risk of thrombosis with risk of bleeding.
1)
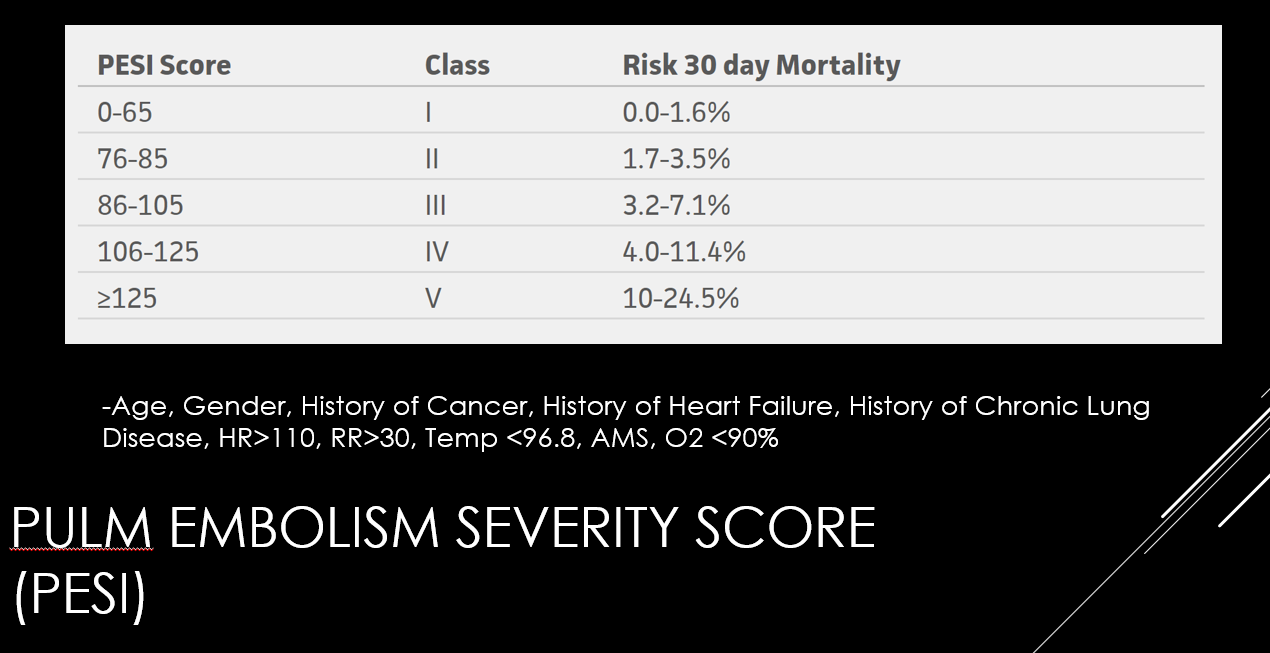
Estimate Thromboembolic Risk
High: Recent stroke, CHADS-Vasc >7/8, Mech heart valve
2)
High Bleeding Risk Procedure (2-4%)
- Coronary Artery bypass, kidney biopsy, neuroaxial, surgery >45min
Low Bleeding Risk Procedure (0-2%)
- cholecystectomy, carpal tunnel repair
Most common autosomal dominant mutation is for Factor V Leiden gene
- Resistance to protein C (inactivates VII and VIII)
- Inactivating the inactivator
Other:
AT III, Protein C and S deficiencies, Antiphospholipid antibody hyperhomocysteinemia
In the surgical patient, there are saboteurs everywhere…even at the microscopic level: Hormone therapy, Obesity, Smoking, Immobilization, Cancer, Trauma
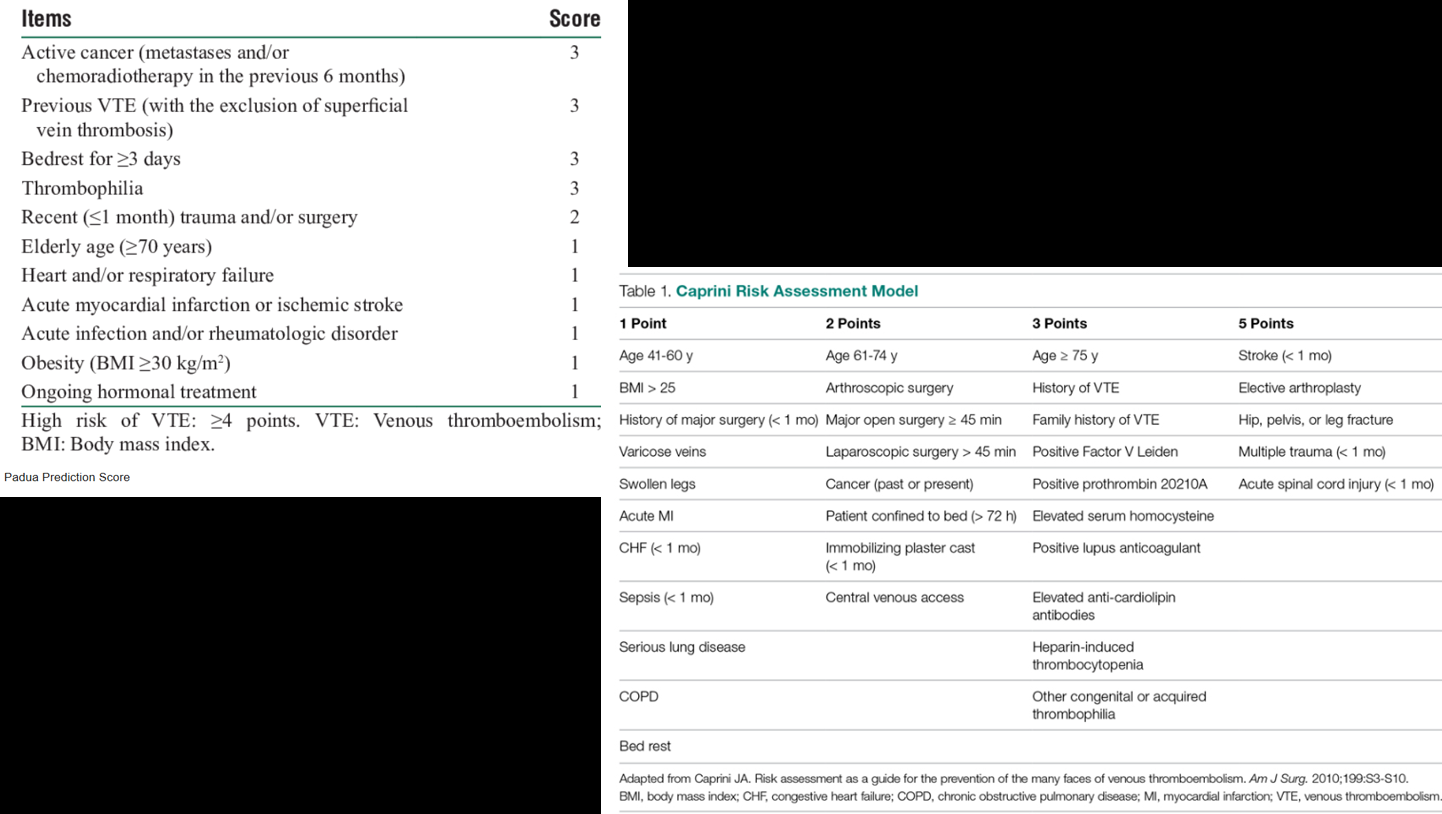
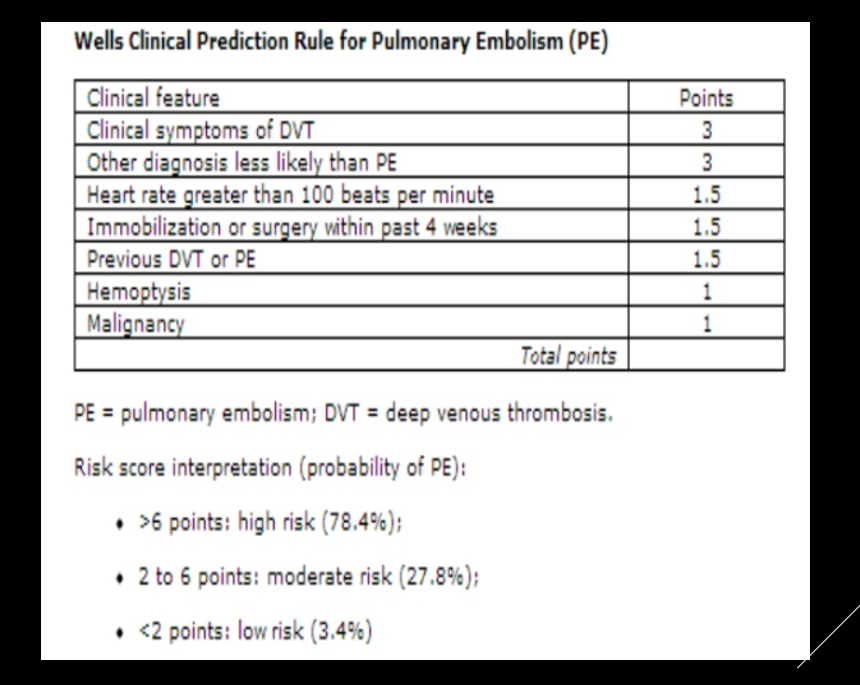
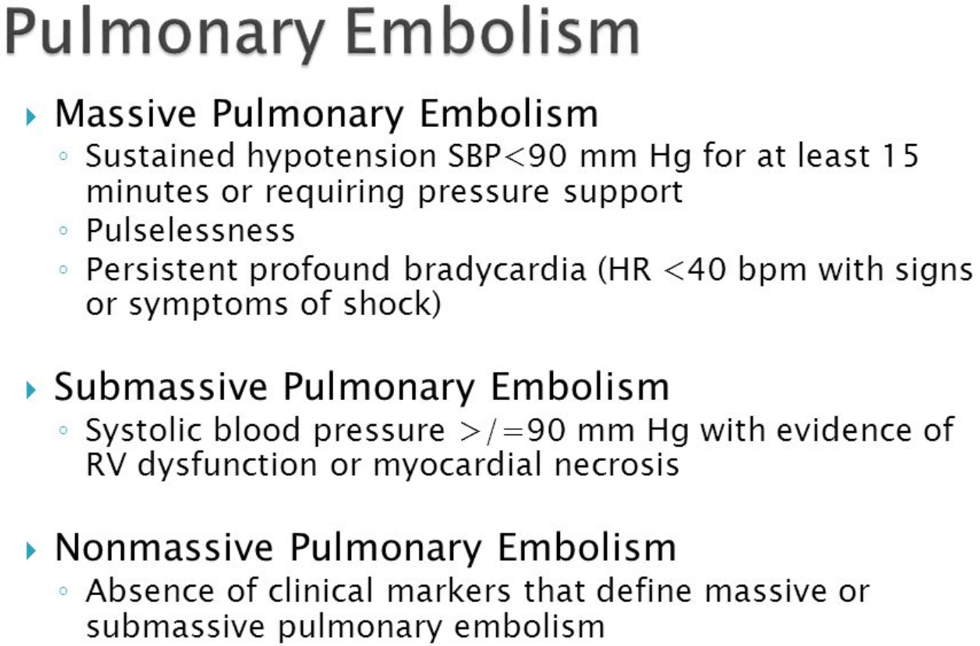
There are several scoring systems that one can use to estimate need for VTE prophylaxis, and risk of a DVT/PE. Below are three such scoring systems (left to right)
Padua (Non Surgical Patient), Caprini (Surgical Patient), Wells
Studies to get
Labs:
D Dimer- 80% sensitive for DVT/ for PE, but not specific. Increased in sepsis, cancer, post operatively
Cardiac markers
Other considerations?
CBC, Coagulation panel, Renal panel
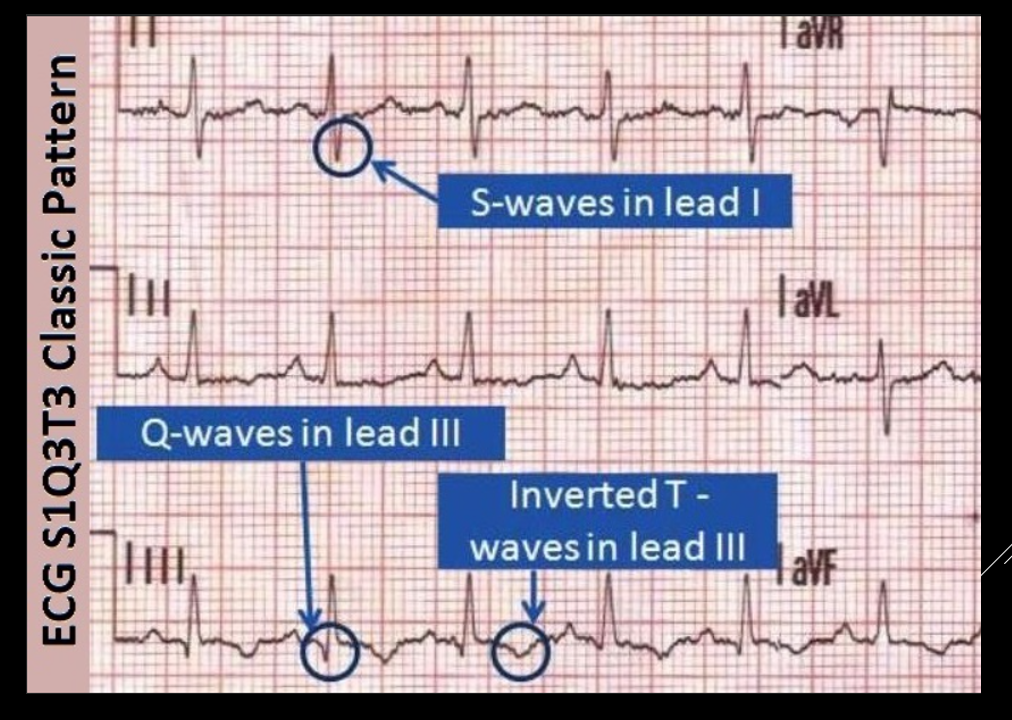
The often tested S3 Q3 T3 is NOT the most common finding on EKGs
RIGHT HEART STRAIN CAN BE SEEN WITH T WAVE INVERSIONS ON V1 to V4
CTA showing a LEFT sided PE.
VQ scan differentiating between normal and high probablity PE. High probabilty PE is defined as 2 or more segmental perfusion defects in the presence of normal ventilation
Non-invasive:
EKG (MC if there is a change is sinus tacch)
Venous ultrasound
Chest CT
Lung scan/VQ scan
ECHO
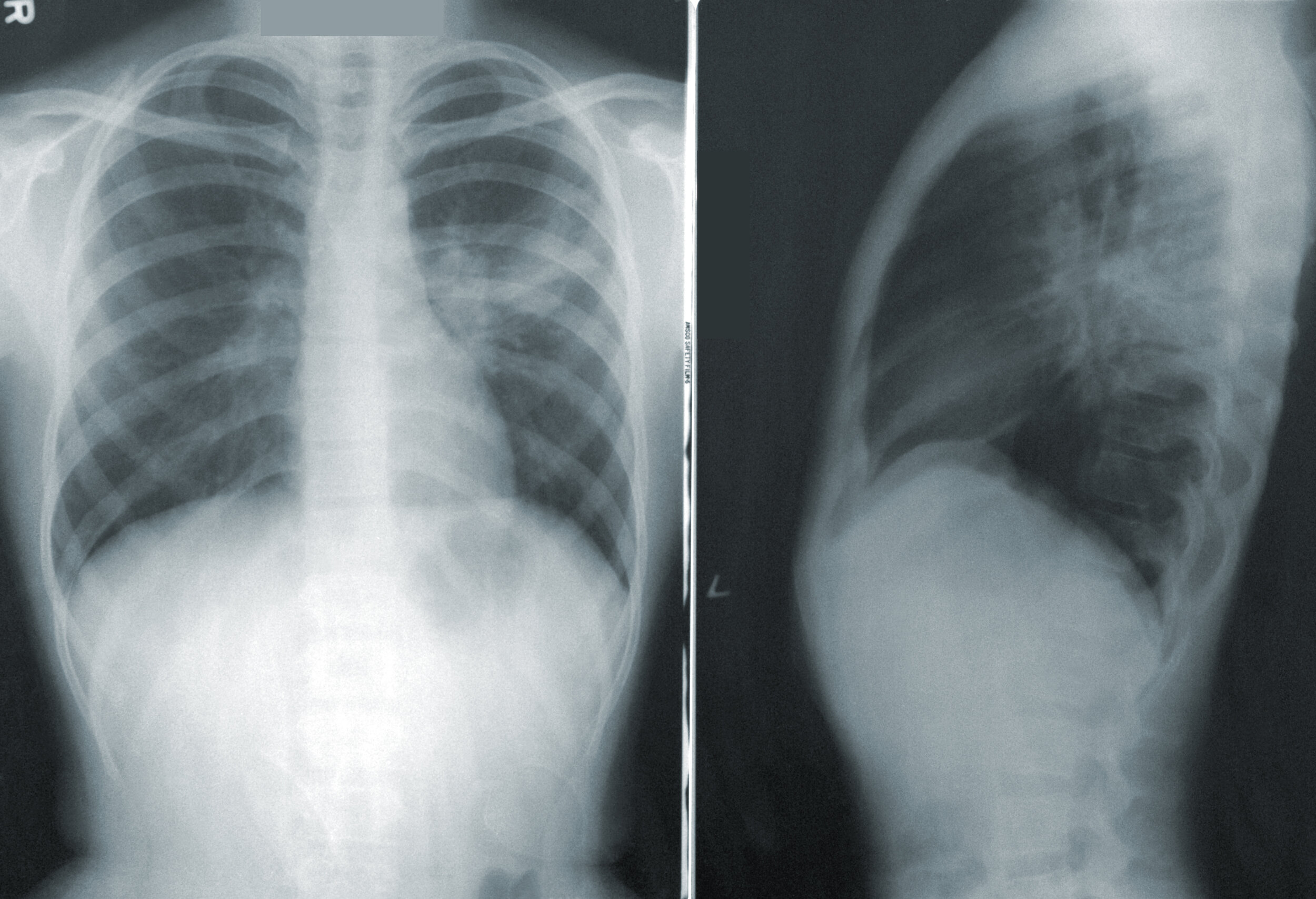
Typically, Chest X Rays in PE patients will be NORMAL. They are used to exclude other pathologies
If there are findings, look for vascular congestion, and infarcted lung
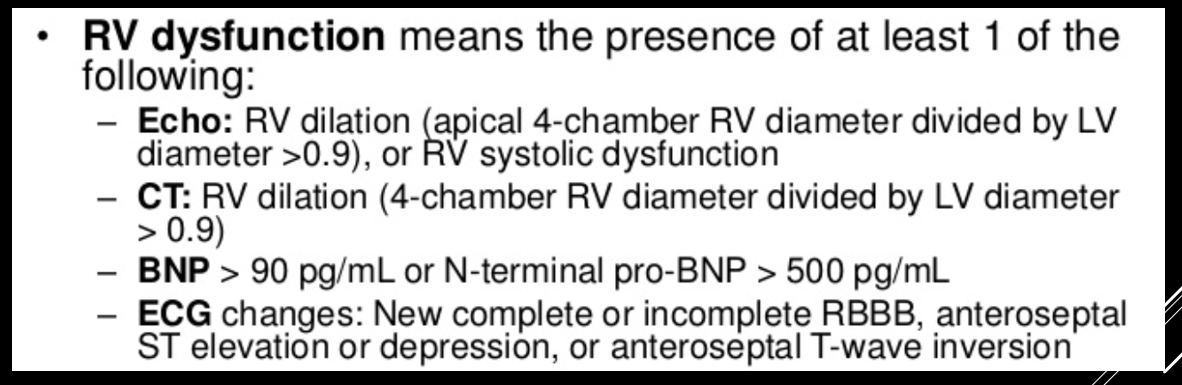
Management Principles:
Resuscitate
Anti-Coagulate
heparin, therapeutic lovenox, direct thrombin inhibitor
will need long term anticoagulation (provoked vs unprovoked vs non-resolution of underlying cause, ie cancer, will determine duration)
Dominate
means of domination include:
IVC Filter (if w/ contraindications to anticoagulation/ consider if w/ prior clots even on anticoag).
OF NOTE IVC FILTERS INCREASE THROMBOSIS
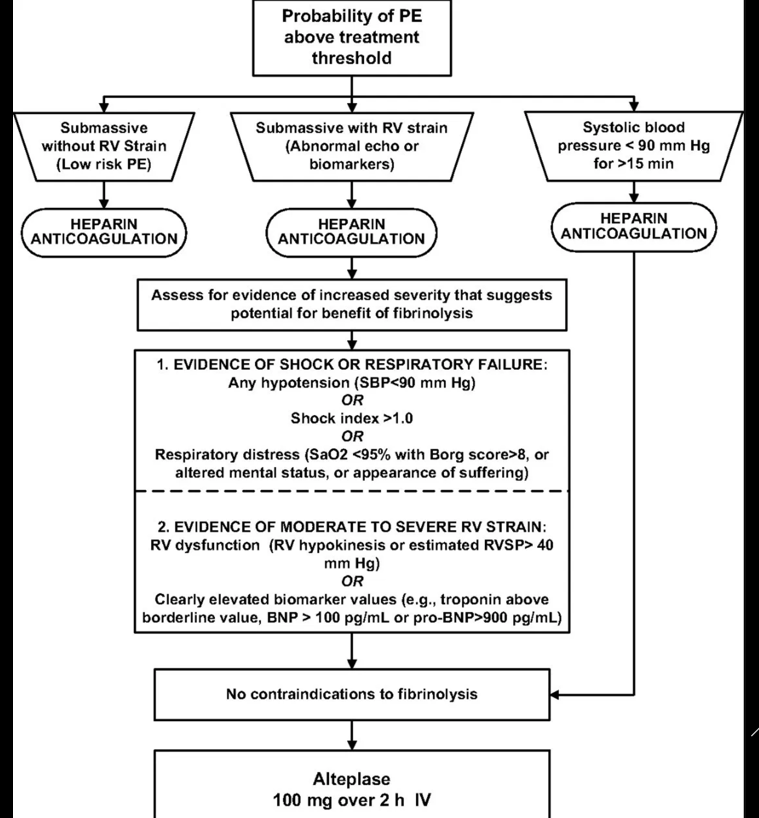
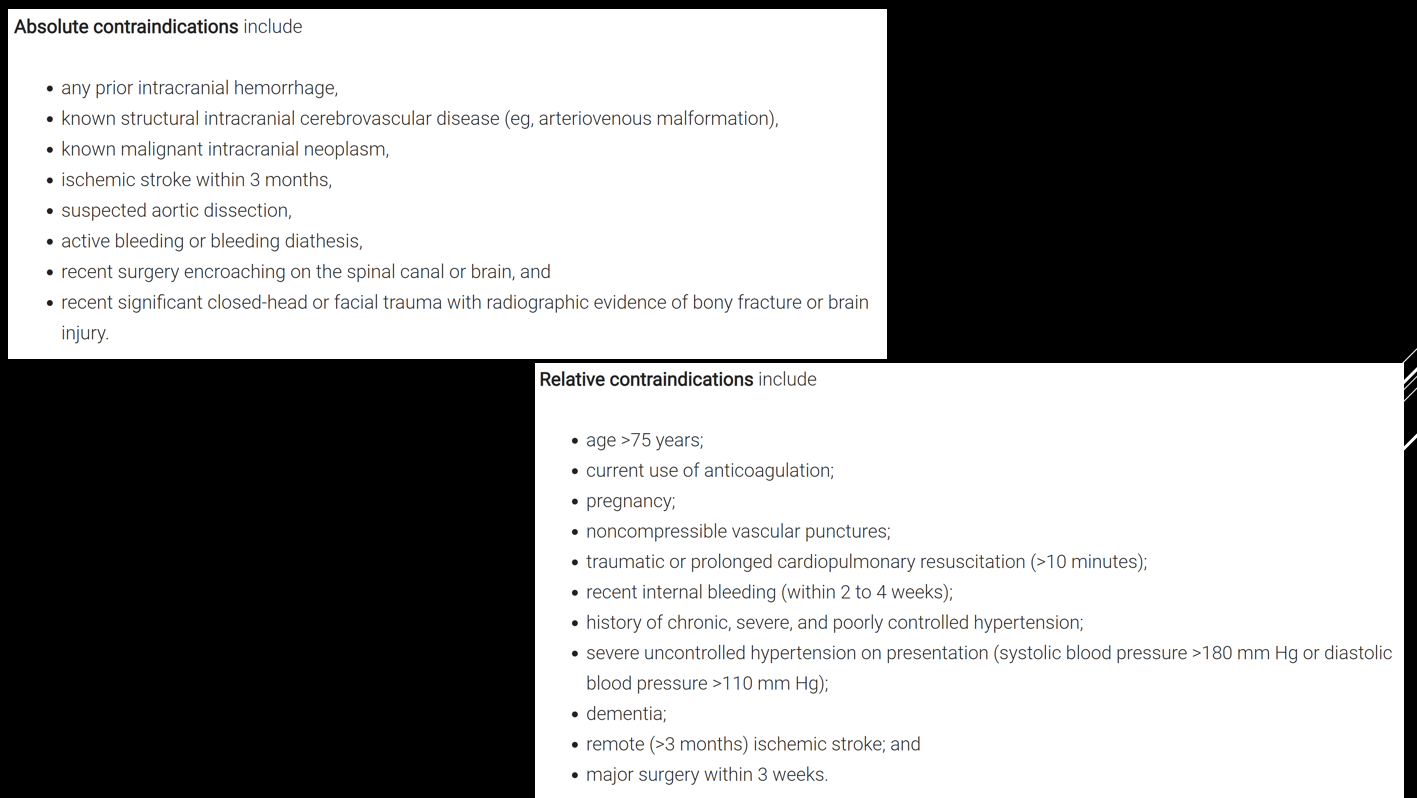
Fibrinolysis (sample algorithm below)