Parathyroid Review
Anatomy
From the 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches
3rd pouch is associated with inferior parathyroid and thymus
Found anteromedially
More likely to be ectopic 🡪 tail of thymus (MC), intrathyroid, mediastinum
4th pouch is associated with superior parathyroid and thyroid complex
Found posterolaterally
Inferior thyroid artery supplies both superior and inferior parathyroids
Hormones
PTH
Increases calcium via:
Kidney reabsorption in DCT
Increase osteoclast activity in bone
Increase Vit D production in kidney (1-OH) 🡪 increase calcium binding in intestine
Also increase PO4- excretion
Vit D
Increases Ca++ AND PO4- via intestine absorption
Calcitonin
Decrease calcium (INHIBITS OSTEOCLASTS)
Increase urinary Ca++ and PO4- excretion
Hyperparathyroidism
Primary
Symptoms reflect changes associated with an increase in calcium
Causes:
Single Adenoma (80%) 🡪 resection
Multiple Adenoma (4%) 🡪 resection
Hyperplasia (15%): Men I and IIa have 4 gland hyperplasia 🡪 subtotal or total + re-implantation
***Adenocarcinoma - rare; can have very high calcium -> radical parathyroidectomy + ipsilateral thyroid lobectomy
** preg: 2nd trimester
** pre-op PTH 🡪 should be ½ of pre-op PTH
** if missing check: “normal” spot, thymus, trachea-esophageal groove, carotids, vertebral body, superior pharynx, thyroid
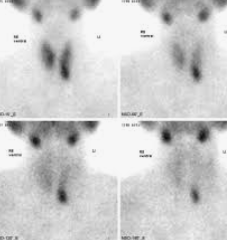
If still missing🡪 sestamibi scan
Persistent hyperparathyroidism🡪 missed adenoma
Recurrent hyperparathyroidism 🡪 new adenoma vs tumor implants
** reop🡪 higher risk of injury
Secondary and Tertiary
2°
Increased PTH 2/2 low Ca (ie in renal failure)
TX: Ca, Vit D, PO4 binder (sevelamer), Cinnacalcet (mimics Ca)// Surgery for bone pain, fx, and pruritus (total + reimplant)
3°
Persistently increased PTH despite “fixing” renal issues
TX: subtotal or total + reimplant
The above is from radiopedia.org
The sestamibi scan is a nuclear medicine study that utilizes Technicium-99-sestamibi. This radio-isotope is taken up by a hyperfunctioning parathyroid gland, and helps with localization.
Special Parathyroid Cases
Pseudo - hypoparathyroidism
Defective PTH receptor in kidney; no response to PTH
Hypercalcemia
90% from hyperplasia/ cancer
Other reasons include: hyperthyroidism, granulomatous disease, Vit D overdose, milk alkali syndrome (high milk/supplement intake), thiazides,
Treatments:
Fluid resuscitation
Calcitonin
Bisphosphonate (does not work immediately)
Steroids (esp if etiology is cancer/granulomatous disease)
*****dialysis if severe******
**Malignancies**
Hematologic (25%) - lytic lesions, low urinary Ca. Ex: multiple myeloma
Non-hematologic (75%) - PTHrP; high urinary Ca. Ex: Squam lung Ca, Breast
Familial Hypercalcemia Hypocalciuria
Increased SERUM calcium. Decreased URINE calcium
2/2 to defective PTH receptor in distal convoluted tubule
TX: nothing. NO parathyroidectomy
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
MEN I
Menin
chromosome 11q3
Parathyroid most common, typically presenting symptom
Pancrease: MC -> gastrinoma; correcting hypercalcemia from hyperparathyroidism may correct this
Pituitary
Correct parathyroid 1st
MEN IIa/b
Ret - protooncogene/MTKR
MTC nears 100%
Pheo is typically b/l + benign
IIB is Badder (B) than IIa
Treatment
Pheo 1st
MTC nears 100%: Prophylactic removal at 6yo (IIa)/ 2yo (IIb)
Parathyroid Cancer
Increase Ca (in the 13’s/14’s) , PTH, and alk phos
Lung mets
Mortality is 2/2 to hypercalcemia. Recur in 50%. MANAGE HYPERCALCEMIA
50% 5 yr mortality
TREATMENT:
Parathyroidectomy + ipsilateral thyroidectomy