Breast Cancer Pt 1
Breast Anatomy
-

Blood Supply
Main Blood Supply of the Breast
Internal Thoracic (or Internal Mammary Artery)
Lateral Thoracic (travels with Long Thoracic Nerve)
Thoraco-acromial artery
Intercostal arteries
-

Lymph nodes
Level I and Level II are taken in Axillary Dissections for Breast Cancer
Level II nodes also known as Rotter’s nodes (posterior to Pec Minor)
Level III is taken in:
Melanoma
Clinically/Pathologic nodes
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
-

Nerves
Long Thoracic- Serratus Anterior (winged scapula)
Thoracodorsal- Latissimus Dorsi (pull up; ADDuction)
Medial Pectoral N- pec major and minor
Lateral Pectoral N- pec major
Intercostal-brachial- 2nd intercostal/medial proximal arm
The American Cancer Society estimates that there are nearly 250,000 new cases of breast cancer yearly in the U.S, and nearly 41,000 deaths from it
Some risk factors include: Female gender (highest risk factor 100:1), age, genetics, fam history, radiation, homonal use (up to 26% increased risk(
Breast cancer metastasizes to BBLL (brain, bone, liver, and lung)
Screening
Typical questions to ask as part of H&P:
Symptoms (Pain? Mass? Skin changes? Nipple discharge? Nipple inversion?)
Age at menarche, age of first pregnancy, fam history of breast cancer, radiation exposure, prior breast biopsies
Average Risk- annual mammogram starting at 40 yo
High Risk- 10 years before youngest age of diagnosis in first degree relative
Risk can be calculated using different risk models/calculators:
NCCN, GAIL, Claus, Tyrer-Cuzick, etc
Symptomatic Breast Work up:
Age <30- US +/- biopsy
Age >30- mammogram +/- US +/- biopsy
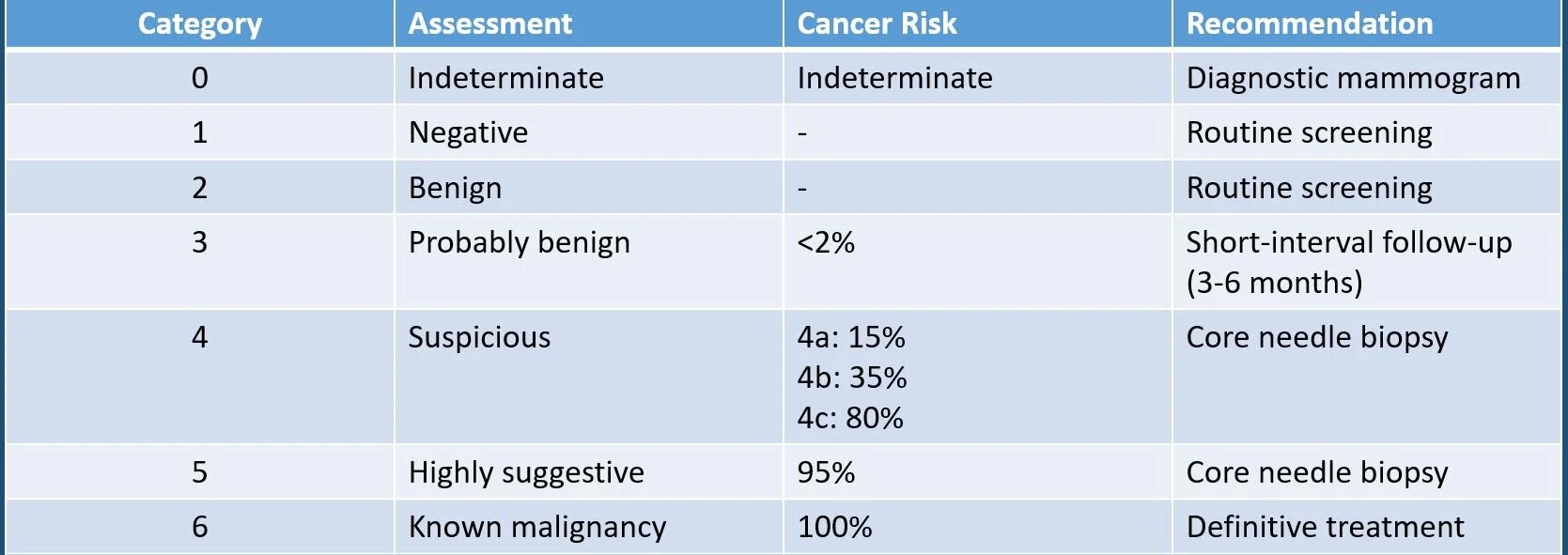
BIRADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) Classification
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
These are malignant ductal epithelial cells that do NOT invade the basement membrane
Pre-malignant lesion that confer:
50% risk of cancer in the ipsilateral breast; 5% in the contralateral breast
Dx: Mammogram; Biopsy
Tx: Lumpectomy (2mm margins) + XRT +/- hormonal therapy
NO SLNB needed
***Mastectomy + SLNB if:
comedo type
multicentric
(persistently) positive margins
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS)
NOT pre-malignant
40% risk of cancer in EITHER breast
Most likely ductal cancer (70%); 5% risk of synchronous lesion at time of diagnosis
Dx: typically incidental
Tx: Excisional biopsy of area (NO MARGINS NEEDED)
+/- tamoxifen
+/- prophylactic mastectomy
Indications for excisional biopsy:
Radial scar
Atypical hyperplasia
LCIS
DISCORDANT PATHOLOGY
*Hyperplasia w/o atypia: 1.5-2x risk
*Atypical ductal or lobular hyperplasia: 4-5x risk
*LCIS: 8-10x risk
GOAL IS NO TUMOR ON INK
Ductal Carcinoma (85%)
most common subtype
TX:
Breast conserving therapy+ SLNB + XRT +/- chemo/hormonal therapy
Modified Radical mastectomy +/- chemo/hormonal therapy
Lobular Carcinoma (10%)
signet ring cells portends worse prognosis
TX:
Breast conserving therapy + SLNB + XRT +/- chemo/hormonal therapy
Modified Radical mastectomy +/- chemo/hormonal therapy
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Sx: Erythema, peau d’orange (from lymphatic invasion)
Dx: full thickness biopsy
NO BREAST CONSERVING THERAPY
Tx: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy then MRM then adjuvant chemo-XRT
SLNB- sentinel lymph node biopsy
XRT- radiation therapy
From AJCC
Contraindications to breast conserving therapy
Breast conserving therapy:
defined as lumpectomy/segmentectomy w/ sentinel lymph node biopsy AND POST OPERATIVE RADIATION THERAPY (XRT)
Goal is NO TUMOR ON INK
***Modified radical mastectomy is defined as taking all breast tissue, the nipple-areolar complex, level I nodes, and level II nodes